Male Sexual Health
Male infertility means a male's inability to cause pregnancy in a fertile female. Approximately, 15% of couples are unable to conceive, even after one year of unprotected intercourse. A male factor is solely responsible in about 20% of infertile couples and contributory in another 30-40%.
Medical factors contributing to Male Infertility:
- Oligo, Astheno, Teratozoospermia
- High DNA Fragmentation Index
- Poor acrosomal capacitation
- Unexplained
- Azoospermia
- Erectile dysfunction
- Anejaculation and Retrograde ejaculation
Grading of Male Infertility based on Semen Analysis:
- 10 M/ml to 15 M/ml - Mild
- 05 M/ml to 10 M/ml - Moderate
- < 05 M/ml – Severe
Correction methods include:
- Hormonal balancing
- Varicocele ligation
- Antioxidants
- Surgical sperm retrieval
- Correction of erectile and ejaculatory disturbances
Consult now to get a holistic analysis, treatment approaches and resolution.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a simple procedure that puts sperm directly inside the uterus, enabling the healthy sperm get closer to the egg. During an intrauterine insemination (IUI) procedure, sperm is placed directly into the uterus using a small catheter. Injection of prepared sperms into the uterine cavity through a fine catheter during peri-ovulatory phase in a natural or stimulated cycle. This is performed, through a fine catheter during peri-ovulatory phase in a natural or stimulated cycle. The objective here, is to improve the chances of fertilization by increasing the number of healthy sperms reach the fallopian tubes, during the most fertile period, in a woman's cycle.
It is predominantly used to treat:
People facing infertility due to medical conditions (e.g., endometriosis or low sperm count or quality), and also couples with unexplained infertility. This procedure is a widely used treatment option because it is a minimally invasive, lower-cost alternative to in vitro fertilization (IVF), and it can be conveniently performed in Dr. Joshi's hospital.
Some key factors requiring IUI include:
- Mild male infertility
- Unexplained infertility
- Mild Endometriosis, Cervical factors
- Erectile dysfunction
How does it help?
- Deposition of large number of motile sperms near the site of fertilisation
- Halves the distance to be travelled by the sperm
- Doubles the probability of fertilisation
Metabolic syndrome refers to the presence of a cluster of risk factors specific for cardiovascular disease. Metabolic syndrome greatly raises the risk of developing diabetes, heart disease, stroke, or all three. Metabolic syndrome includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist and abnormal cholesterol levels. The syndrome increases a person's risk of heart attack and stroke.
Threats for Male Fertility
This condition may result in hypogonadism, increased scrotal temperatures, impaired spermatogenesis, decreased sperm count, leading to about 50% of cases of couple infertility worldwide. The condition or in medical terms, the pathophysiology involves a complex crosstalk of psychological, neuromuscular, endocrinological, and vascular factors along with their correlations with several lifestyle habits like cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption and sometime due to some drug side effects.
This condition is primarily detected by the presence or indications of:
- Abdominal obesity
- High blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury) or higher.
- Impaired fasting blood glucose
- High triglyceride levels of more than 150 mg/dL
- Low HDL (good) cholesterol
In addition to changing one's lifestyle, and adopting healthy practices including meditation, yoga, exercise or therapy, one needs to consult an expert Andrologist, to seek specific guidance and line of treatment is crucial in addressing this syndrome. The Andrologist can provide a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment methods.
PART 1
There are many established and recommended methods to treat Erectile Dysfunction from medication, surgery, therapy, exercises, testosterone replacements, penile implants, psychological counseling and more. Medical management, penile injections, vacuum devices, penile surgeries with implants are diverse methods used to treat the condition.
A penile implant is an implanted device intended for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. A penile implant is an erection assistance device that is designed to help a man get an erection and is completely hidden inside the body. There are many factors governing the approach to penile implants. If the person does not respond adequately to medication, if the outcomes of medical management are insufficient or cannot sustain, surgical intervention for penile erection, penile prosthesis or implants, is the suggested route.
The person must be declared, in medical terms, as a case of Refractory Erectile Dysfunction, if he does not respond to any of the treatment methods. Usually, the implants are then recommended for males above 30 years.
Cultural framework impacts treatment of Erectile Dysfunction
In Western countries, sex and sex-related issues or challenges are openly discussed and addressed. In India, sex continues to be a taboo, sex-related health issues and treatment methods are still inhibited. Most men refuse to discuss it openly, admit it even to themselves, thereby, allowing the issue to persist or continue.
In the Indian society, even women are protective about their partner's or husband's sexual health. The perception is that the man should not undergo any surgery or procedure, with an assumption that there is no medical condition. Unfortunately, they do reach out for medical intervention much later, when the case has reached a state of irreversibility.
Benefits of Implants
Among the benefits of Implants, an important one is that it enables a more spontaneous sex life that requires no external devices or tools. One can resume sexual activity four to six weeks after penile implant surgery. Post surgery, the erection looks and feels natural, and more significantly, does not change sensations during sex or the ability to climax. This gives not only physical relief, satisfaction and happiness, it also rebuilds confidence, and relieves stress from the individual. Unlike other treatments for erectile dysfunction (ED), a penile implant restores spontaneity and allows a man to get an erection without any planning or waiting. The device is implanted during a procedure through a small opening in the skin.
Reconstructive urology is surgery to restore normal function by repairing, rerouting, or recreating areas of the upper and lower urinary tract and some reproductive organs. Genital and pelvic reconstruction aims to restore normal anatomy and function of the genitourinary tract.
Reconstructive urologic surgery involves the treatment of the problems that patients may suffer from after the treatment of urologic and pelvic cancers or after trauma sustained to the urinary tract.
Some of the commonly managed diagnoses include:
- Urethral strictures
- Management of hypospadias complications
- Ureteral strictures
- Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- Urinary tract fistulas
- Urinary Incontinence
- Erectile dysfunction
- Complications of prior surgery
Reconstructive urologic surgery can restore normal function after damage or disease of the penis, prostate, scrotum, testes, or urinary tract, which includes the:
In the Indian society, even women are protective about their partner’s or husband’s sexual health. The perception is that the man should not undergo any surgery or procedure, with an assumption that there is no medical condition. Unfortunately, they do reach out for medical intervention much later, when the case has reached a state of irreversibility.
- Kidneys, where urine is made
- Ureters, the tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder
- Bladder, where urine is stored
- Urethra, the tube through which urine exits the body
Connect with our Centre for an appointment.
Placement of an inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) is the mainstay of surgical treatment for patients with erectile dysfunction (ED). The management of ED usually starts with clinical assessment, lifestyle changes, and modifying drug therapy that may cause ED. The treatment follows a sequential process covering medication to surgical intervention, subject to patient’s degree and level of improvement.
Firstly, pharmacotherapy is administered usually, with oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. If these treatments are not successful, vacuum constriction devices, intraurethral alprostadil, and intracavernous injection of a vasoactive drug are available as second-line treatments, followed by penile prostheses (PP) as a third-line treatment. Inflatable penile prostheses are the most commonly implanted devices for medically refractory ED patients and for those with contraindications to pharmacotherapy.
However, loss of penile size is a common complaint that can negatively affect patient satisfaction rates following successful penile prosthetic implant surgery. Strategies to preserve and potentially increase penile size are of great importance to all implanters. As with other sexual dysfunction therapies, the outcome of PPI surgery is largely dependent on patient and partner satisfaction. Most frequent implanters will realize that perceived inadequacy of penile size, be it penile girth or penile length, are practical issues that need to be addressed in clinical practice, and may be best suited for a full discussion pre-operatively, to set realistic expectations.
It is noted that IPPs are superior to malleable implants in attaining greater postoperative penile lengths and girths. Post- operative penile length was 6.37 times more likely to rise above preoperative post-ICI stretched length in inflatable penile implants compared to malleable implant cases (12.5% vs 1.96%) (P value=0.0105). IPPs were 2.5 times more likely to increase the girth of the penis (27.2% vs 10.9%) (P value <0.05). IPPs were 2.1 times less likely to cause a decrease in circumference in comparison to malleable implants (9.1% vs 19.2%) (P value <0.05).
Revision surgery due to implant dissatisfaction was observed as least in IPP. Hence it is a viable option for those experiencing ED, as advised by the specialist.
Penile implants are considered when other methods of restoring erection capabilities and functions are unresolved. Typically, Inflatable penile implant: A pump in your scrotum (the pouch of skin behind your penis) allows you to get an erection whenever you choose.
In this type of inflatable penile implant, the surgeon inserts the cylinders into the penis. Tubes connect the cylinders to a separate reservoir under the lower abdominal (stomach) muscles. The reservoir contains fluid and a pump connects to this system. It is placed under the loose skin of the scrotum, between testicles. It is built for long lasting, and is risk-free, does not get subjected to mechanical failures.
Key benefits include:
- The implant is closest to the physiological erections
- Provides better rigidity
- Greater satisfaction rate among couples
- Lesser dissatisfaction rate
- Better chances of length and girth preservation
Overall, it is said to enhance confidence in the individual’s ability to engage in sexual activity.
Sperm health depends on various factors, including quantity, movement and structure.
What is normal semen and how can I judge my sperm count from it?
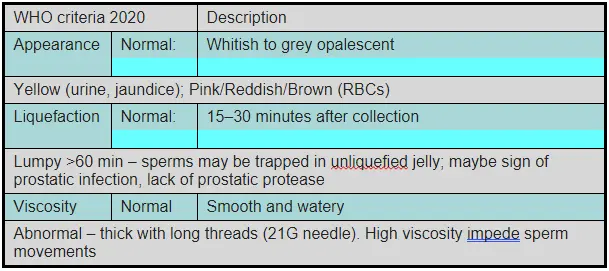
Normal semen has several characteristics including physical, chemical, and microscopic properties. As a man you can only see the physical properties of ejaculation but their alteration in itself is not enough to define the normal from the abnormal. Normal semen volume ranges from 1.5 to 5 millilitres per ejaculation. Which means that usually you will ejaculate about one third to a teaspoon full of semen. The more excited you are, the more will be the ejaculated volume.
Sperm Colour
Typical colour is whitish-grey. Variations can occur, but significant deviations may indicate health issues. Anything red, yellow or brown is a matter of concern and you should be found next in an andrologist's cabin if you notice that.
Sperm Density
Semen is usually thick and viscous upon ejaculation but liquefies within 20-30 minutes. If it does not liquify or liquifies later than that then its again a problem waiting to be solved by an andrologist.
Sperm Odour
Semen typically has a mild, slightly chlorine-like smell often also described as a fishy smell. Foul smell indicates infection and merits a visit to a doctor.
Semen is supposed to be viscous but very thin semen or too viscous a semen can be something to worry about, especially if there is a sudden change in consistency.
Beyond this a normal person cannot judge anything more from the semen. Many other chemical properties and the microscopic qualities like presence of sperms, and other cells cannot be done by the naked eye. So it is time to understand one’s sense of fertility potential by just looking at one’s own semen grossly.
It is good to be aware that no one (not even doctors) can differentiate between a fertile and an infertile man just by looking at their semen samples.
A semen checkup, also known as a semen analysis, can be an important diagnostic tool for assessing male fertility and reproductive health. Here are some situations when you might consider undergoing a semen checkup:
Infertility Concerns:
If you and your partner have been trying to conceive for a year or more without success, it's advisable for both partners to undergo fertility evaluations, including a semen analysis for the male. If you partner’s age is more than 35 years then you can consider this analysis even after 3-6 months of trying.
Preconception Planning:
If you are planning to start a family and want to check your fertility status to identify any potential issues early. In this case you can go for a pre-marital health checkup where the andrologist will do an examination for you along with semen analysis and evaluation of your testosterone levels.
Post-Vasectomy Confirmation:
After a vasectomy, a semen analysis is necessary to confirm the absence of sperm in the ejaculate, ensuring the procedure was successful. It typically takes 3 months or at least 20 ejaculations to get rid of the stored sperms.
Post-Vasectomy Reversal:
If you have had a vasectomy reversal, a semen analysis will help determine if sperm is present and in what quantity, indicating the success of the procedure.
Known Reproductive Issues:
If you have a medical history or symptoms that could affect fertility, such as undescended testicles, varicocele, hormonal imbalances, or infections you can go for a semen checkup to detect abnormalities early and start treatment in time.
Unexplained Symptoms:
If you experience symptoms like pain, swelling, or lumps in the testicular area, changes in sexual function, or abnormalities in ejaculate (e.g. colour, consistency) as discussed earlier
Health Conditions:
Certain health conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or autoimmune diseases can affect fertility. A semen analysis can be part of managing and monitoring these conditions.
Lifestyle Factors:
If you have been exposed to environmental toxins, excessive heat (like frequent use of hot tubs), or have habits like smoking, heavy alcohol use, or drug abuse that might affect sperm quality it will be good to check your semen if you are planning or intend to plan your family in the coming future.
Medical Treatments:
If you are about to undergo treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy, which can impact fertility, a semen analysis can help assess the need for sperm banking and is highly recommended by oncologists.
Consulting with a healthcare provider or a fertility specialist can help determine the necessity and timing of a semen checkup based on your specific circumstances and health status. The above-mentioned points are indicators or triggers for you to visit.
Normal sperm have a specific structure that can be observed under a microscope. Here are the key characteristics of normal sperm morphology:
Sperm Structure
The sperms are made up of three sections, the head, the midpiece and the tail. The head is oval and smooth, approximately 5-6 micrometres long and 2.5-3.5 micrometres wide. The front part of the head is called acrosome, which contains chemicals necessary for penetrating the egg. It covers about 40-70% of the head's surface. The head should not be too large or too small and should have an oval shape without any irregularities.
Then there is a cylindrical midpiece that should be of uniform width. It is packed with mitochondria that provide energy for the sperm's movement. This midpiece should be approximately the same length as the head and connected seamlessly to it. Midpiece should be straight, not bent or kinked, and should be attached correctly to the head.
The last part is the tail or the flagellum which is Long and thin, about 45 micrometres long, several times the length of the head and midpiece combined. It provides propulsion through a whip-like motion, enabling the sperm to swim towards the egg. The tail should be single and straight, without any bends or coils. It should not be broken or significantly shorter or longer than normal.
To visualize, a normal sperm can be imagined as a tadpole:
Head: Like the head of the tadpole, oval and smooth
Midpiece: A short section immediately behind the head.
Tail: Long and slender, resembling the tail of the tadpole, enabling swimming
Maintaining a high percentage of normal sperm morphology is important for male fertility, as it increases the likelihood of successful fertilisation. This can be found out by getting a semen analysis done.
A semen analysis, also known as a sperm count, is a laboratory test that evaluates a man's fertility by measuring the quality and quantity of his semen and sperm.
Typically this is what a normal report would look like:
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens, can help protect sperm from oxidative damage.
- Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and improve overall health. However, avoid excessive exercise, which can negatively impact sperm quality.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, as dehydration can affect semen volume and sperm health.
- Reduce alcohol intake, as excessive drinking can lower testosterone levels and reduce sperm production.
- Quit smoking and avoid recreational drugs, as these can impair sperm quality and reduce fertility.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as hot tubs, saunas, and tight clothing, which can negatively impact sperm production.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises. Chronic stress can negatively affect hormone levels and sperm quality.
- Minimize exposure to environmental toxins and chemicals, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial pollutants, which can harm sperm health.